Amanita mushroom gummies vs. Psilocybin gummies – Key differences
In the expanding world of fungi-based supplements, two types of mushroom gummies have gained significant attention – those made from Amanita muscaria and those containing psilocybin. While both originate from the fungal kingdom and are often discussed in the context of consciousness alteration, these two varieties of gummies differ substantially in their composition, effects, legal status, and potential applications.
Chemical composition
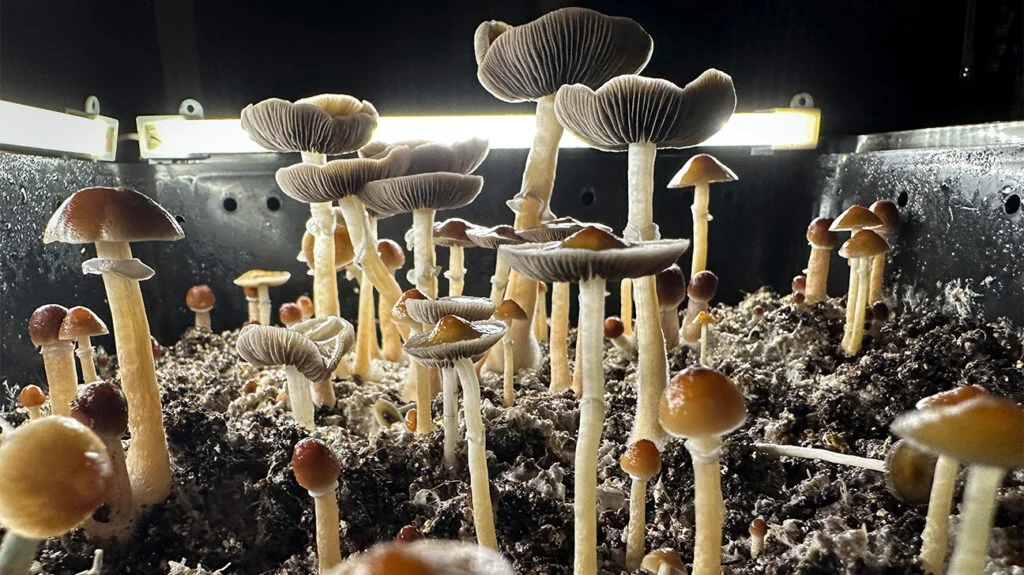
The most fundamental difference between these gummies lies in their active compounds. Amanita muscaria gummies contain muscimol and ibotenic acid as their primary psychoactive components. Muscimol acts as a powerful agonist of GABA receptors, enhancing GABA effects, the primary inhibitory neurotransmitter in the brain. Ibotenic acid, present in raw Amanita muscaria, is typically converted to muscimol during preparation.
In contrast, psilocybin gummies derive their effects from psilocybin and its active metabolite, psilocin. These compounds share structural similarities with serotonin and predominantly influence serotonin receptors in the brain, particularly the 5-HT2A receptor. This fundamental difference in chemical action is responsible for the distinct effects associated with each gummy type.
Effects on consciousness
Users of these two types of gummies report markedly different experiences. Amanita muscaria gummies produce a dreamy, sedative-like state. Users may experience altered perception, detachment from reality, and, in some cases, vivid dreams or dreamlike waking states. The impact can vary from gentle relaxation to significant awareness changes, influenced by the dosage and individual responsiveness.
Psilocybin gummies are known for producing what many describe as a classic psychedelic experience. This includes visual and auditory hallucinations, altered perception of time and space, intense emotional experiences, and sometimes profound insights or mystical-type experiences. Psilocybin frequently induces powerful effects that result in notable shifts in thinking and perception.
Duration and onset of effects
The timeline of effects also differs between these two types of gummies. amanita mushroom gummies typically have a slower onset, with effects beginning to manifest anywhere from 30 minutes to 2 hours after consumption. Users can expect the effects to persist for 5 to 10 hours, with occasional reports of lingering effects extending into the following day.
Psilocybin gummies generally have a faster onset, with effects often becoming noticeable within 20 to 40 minutes. The peak of the experience usually occurs within 2 to 3 hours, with the entire journey typically lasting 4 to 6 hours. However, the duration can vary based on factors such as dosage and individual metabolism.
Research and therapeutic potential
The research landscape for these two substances differs considerably. Psilocybin has garnered significant attention in recent scientific research, particularly for its potential to address conditions such as depression, anxiety, addiction, and PTSD. Numerous reputable institutions are actively conducting clinical trials on psilocybin, reflecting a burgeoning interest in its therapeutic possibilities.
Research on Amanita muscaria, and specifically on muscimol, is comparatively limited. While there’s historical and anecdotal evidence of its use in traditional practices, modern scientific studies on its potential therapeutic applications are scarce. Early research has explored muscimol’s potential for treating epilepsy and sleep disorders, though these studies are in their infancy compared to research on psilocybin.