Understanding the Role of Physical Therapy in Post-Stroke Recovery
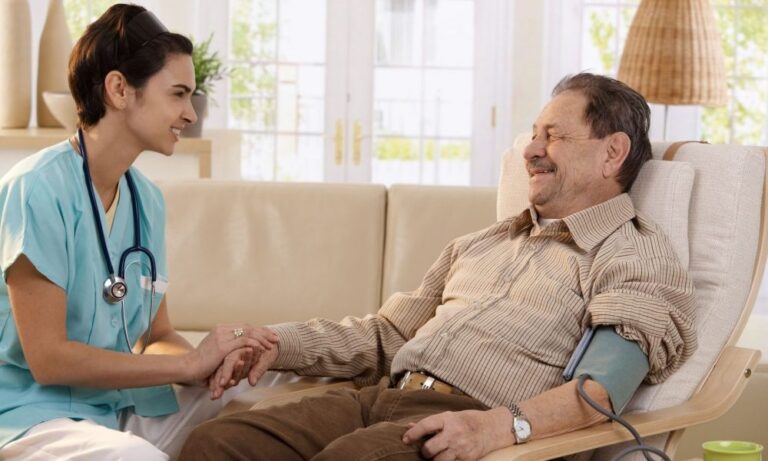
A stroke is a life-altering event that can leave survivors with significant physical and cognitive impairments. The journey to recovery can be long and challenging, but with the right support, many individuals can regain function, improve mobility, and enhance their quality of life. Physical therapy is a critical component of post-stroke rehabilitation, helping survivors recover strength, coordination, and independence.
At Control Physical Therapy, we provide specialized rehabilitation programs designed to address the unique challenges stroke survivors face. In this blog, we explore the vital role physical therapy plays in post-stroke recovery and how it helps patients on their road to recovery.
1. Addressing Physical Impairments
Strokes often lead to muscle weakness, paralysis, and loss of coordination, usually on one side of the body. These physical impairments can make it difficult to perform basic daily tasks such as walking, dressing, or even standing. Physical therapy focuses on restoring muscle strength, improving coordination, and regaining mobility.
Therapists work with stroke survivors to help them:
- Strengthen weakened muscles through targeted exercises
- Relearn motor skills needed for everyday activities
- Improve balance to reduce the risk of falls
These therapies help survivors regain physical function and independence, making it possible to return to daily life with greater ease.
2. Improving Mobility and Gait
For many stroke survivors, mobility issues are a major challenge. A common symptom following a stroke is difficulty walking due to muscle weakness or impaired coordination. Physical therapy uses gait training and mobility exercises to help patients regain the ability to walk independently or with minimal assistance.
Therapists may use tools like:
- Assistive devices such as canes or walkers to support walking
- Balance exercises to improve stability and prevent falls
- Strengthening exercises to improve control of the legs and core muscles
Over time, this training can lead to significant improvements in mobility, helping stroke survivors move more confidently and safely.
3. Enhancing Flexibility and Range of Motion
Stiffness and spasticity (involuntary muscle contractions) are common after a stroke, particularly in the arms and legs. Physical therapy focuses on improving flexibility and range of motion through stretching exercises and manual therapy techniques. These exercises help reduce muscle stiffness and promote smoother, more coordinated movements.
By addressing spasticity and restoring flexibility, therapists help stroke survivors regain control over their body movements, allowing for a more functional recovery.
4. Regaining Fine Motor Skills
Many stroke survivors experience a loss of fine motor skills, which can affect their ability to perform precise tasks such as buttoning a shirt, holding utensils, or writing. Physical therapy includes exercises that specifically target the smaller muscles in the hands, wrists, and fingers, helping to rebuild dexterity and coordination.
Through repetitive movements and strength training, patients can gradually improve their ability to perform fine motor tasks, leading to greater independence in daily activities.
5. Cognitive and Emotional Support
Physical therapy not only addresses physical impairments but also offers emotional and cognitive support for stroke survivors. A stroke can affect an individual’s ability to process information, concentrate, and solve problems. In some cases, survivors may also experience anxiety, depression, or frustration related to their recovery process.
Therapists at Control Physical Therapy work closely with patients to encourage mental resilience and provide support during rehabilitation. This holistic approach helps survivors stay motivated and committed to their recovery journey.
6. Long-Term Rehabilitation and Prevention of Future Strokes
Stroke recovery is often a long-term process that requires continuous rehabilitation. Physical therapy is designed to adapt to each phase of recovery, evolving as the patient progresses. Additionally, physical therapy helps patients reduce the risk of future strokes by encouraging lifestyle changes such as increased physical activity, weight management, and cardiovascular health.
Therapists educate stroke survivors on how to maintain their progress and prevent future strokes through:
- Home exercise programs that promote continued strength and mobility
- Healthy lifestyle recommendations to manage risk factors like hypertension or diabetes
- Ongoing support to address any setbacks or challenges during recovery
Conclusion
Physical therapy plays a central role in helping stroke survivors regain independence, improve mobility, and rebuild strength after a stroke. By addressing physical impairments, improving mobility, and offering emotional support, physical therapists help patients take meaningful steps toward recovery.
At Control Physical Therapy, we understand the challenges stroke survivors face, and we are committed to providing compassionate, evidence-based care to support every phase of recovery. If you or a loved one is recovering from a stroke, contact us today to learn how our customized physical therapy programs can help you regain control of your life and improve your overall well-being.