Understanding Diabetic Eye Disease Treatment: Restoring Your Vision
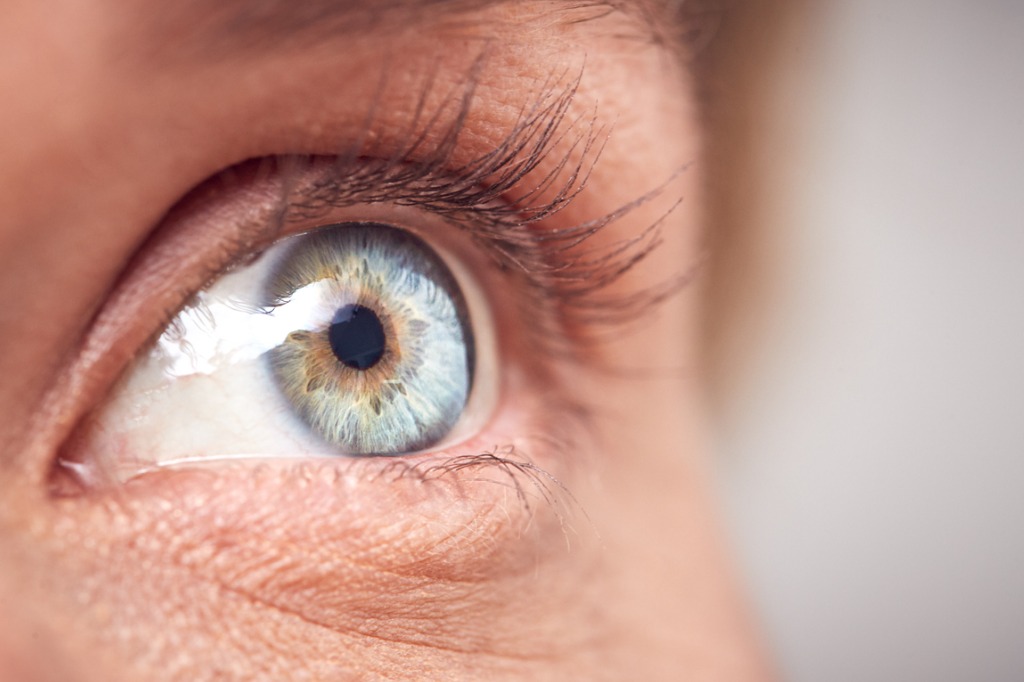
Diabetic eye disease, primarily diabetic retinopathy, is one of the leading causes of vision loss in people with diabetes. High blood sugar levels can damage the blood vessels in the retina, leading to various eye problems. Fortunately, there are several treatment options available to help restore vision and prevent further deterioration.
Early diagnosis and intervention are key to preserving sight, and this article will explore the treatment options available for diabetic eye disease and how they help restore vision.
What is Diabetic Eye Disease?
Diabetic eye disease encompasses several conditions that can affect the eyes of people with diabetes, including diabetic retinopathy, diabetic macular oedema (DMO), and cataracts. The most common is diabetic retinopathy, which occurs when high blood sugar levels cause damage to the tiny blood vessels in the retina.
This can lead to leakage of blood and fluid, causing vision impairment. The disease progresses in stages, starting with mild changes that may go unnoticed, leading to severe vision loss if untreated.
The Importance of Early Detection
The key to diabetic eye disease treatment is early detection. In the early stages of diabetic retinopathy, patients may not experience any symptoms, making it critical for individuals with diabetes to undergo regular eye exams. By detecting the disease before it causes significant damage, doctors can initiate treatment to prevent vision loss.
Early intervention can also reduce the risk of developing complications, such as diabetic macular oedema, where the macula, the central part of the retina, becomes swollen and affects sharp vision.
Available Treatment Options
Laser Treatment (Laser Photocoagulation)
One of the most common treatments for diabetic eye disease is laser photocoagulation. This procedure uses a laser to target and seal off leaking blood vessels in the retina, which helps to prevent further damage and stabilizes vision.
Laser is used as a treatment for proliferative diabetic retinopathy and diabetic macular oedema
The procedure is typically done in an outpatient setting and has minimal side effects.
Anti-VEGF Injections
Anti-VEGF (vascular endothelial growth factor) injections are used primarily to treat diabetic macular oedema (DMO), a condition where fluid leaks into the retina, causing it to swell and impair vision.
Anti-VEGF therapy works by blocking the VEGF protein, which stimulates the growth of abnormal blood vessels in the retina.
These injections can significantly reduce the swelling in the retina, leading to improved vision. The injections are typically administered in a series, with the frequency of treatment depending on the patient’s condition.
Vitrectomy Surgery
In more advanced cases of diabetic retinopathy, where the retina has become severely damaged, a vitrectomy may be necessary. This surgical procedure involves removing the vitreous gel from the eye, which may contain blood or scar tissue, and replacing it with a saline solution.
Vitrectomy can improve vision by clearing the eye of blood and debris, but it is generally reserved for severe cases such as long standing non clearing vitreous haemorrhage or tractional retina detachment.
Steroid Injections and Implants
In some cases, corticosteroids may be injected into the eye to reduce inflammation and control diabetic macular oedema. These injections help reduce swelling in the retina and can improve vision in certain patients. In addition, steroid implants, which slowly release medication over time, may also be used to manage DME.
Managing Diabetic Eye Disease Through Lifestyle Changes
While diabetic eye disease treatment focuses on medical interventions, managing blood sugar levels is equally important in preventing further eye damage. High blood sugar levels contribute to the deterioration of blood vessels in the retina, so maintaining a healthy glucose level can slow the progression of the disease.
Managing blood pressure, cholesterol levels, and quitting smoking can also help reduce the risk of diabetic eye disease. A balanced diet, regular exercise, and adherence to diabetes medications are key factors in maintaining overall health and preventing complications.
Conclusion
Diabetic eye disease is a serious condition that can lead to permanent vision loss if left untreated. However, with early detection and appropriate diabetic eye disease treatment, many patients can prevent severe damage and even restore their vision.
Treatment options such as laser therapy, anti-VEGF injections, and vitrectomy surgery have proven effective in managing the disease.
Alongside medical interventions, lifestyle changes and regular eye exams play a crucial role in ensuring long-term eye health. If you have diabetes, don’t neglect your eye care – early intervention is key to preserving your vision.