Lymphedema Treatment with Multi-Layered Compression
Lymphedema is a chronic condition that affects millions of people worldwide, causing swelling, discomfort, and limited mobility, most commonly in the arms and legs. If you or a loved one are living with lymphedema, it’s important to know that effective treatments are available—and one of the most proven methods is multi-layered compression therapy. In this blog, we’ll explore what lymphedema is, how multi-layered compression works, why it’s considered a gold standard in lymphedema management, and best practices for successful treatment.
What is Lymphedema?
Lymphedema is characterized by the accumulation of lymphatic fluid in the tissues, leading to swelling and discomfort. It commonly arises after lymph node removal or damage during cancer treatment, surgery, or trauma. Without proper management, lymphedema can worsen over time, causing pain, skin changes, and increased risk of infections.
Why Compression Therapy is Essential in Lymphedema Management
Compression therapy is a cornerstone in lymphedema treatment because it helps move lymph fluid out of the affected limb, reduces swelling, and improves lymphatic drainage. Among the various forms of compression, multi-layered compression has emerged as the most effective method supported by clinical research and patient outcomes. Multi-layered compression provides graduated, sustained pressure, which is essential for preventing fluid buildup and reducing limb volume.
What is Multi-Layered Compression?
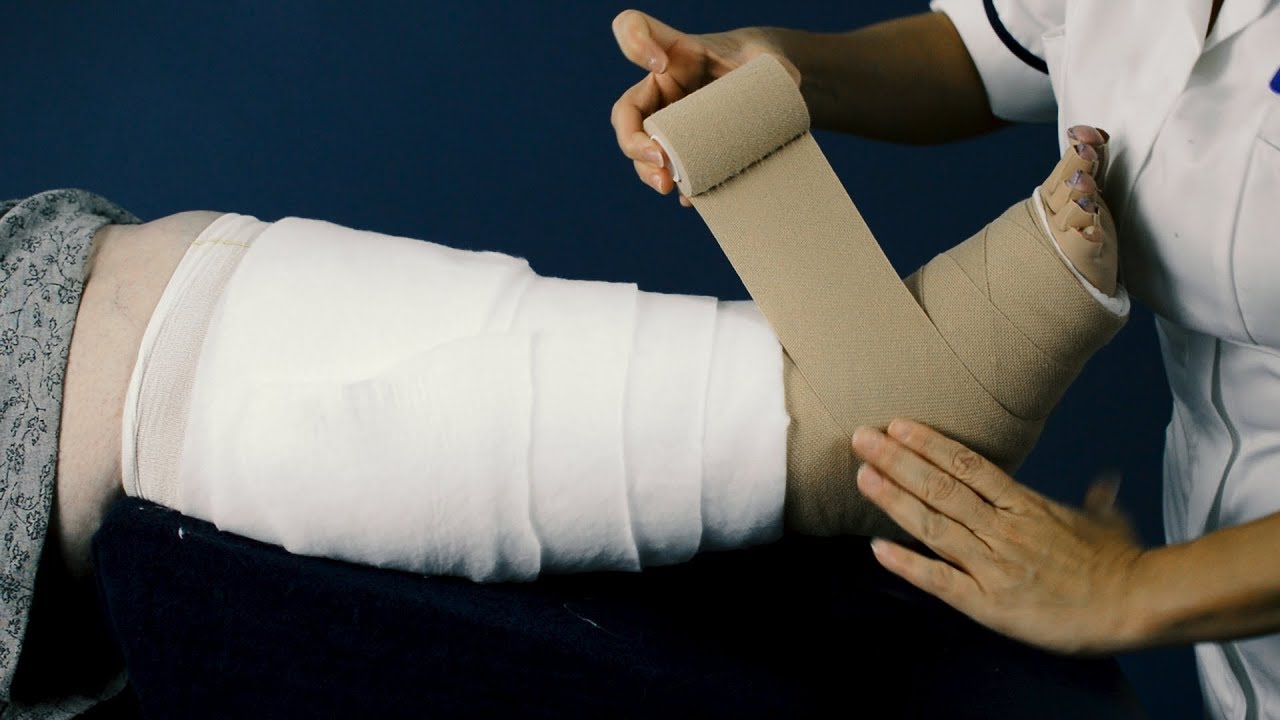
Multi-layered compression involves applying several layers of specialized bandages or wraps to the affected limb. Each layer serves a specific purpose:
- Padding Layer: Protects delicate skin, distributes pressure evenly, and fills in anatomical gaps to prevent bandage slippage.
- Absorbent Layer: Manages excess fluid, keeping the skin dry and reducing the risk of infection.
- Short-Stretch Compression Bandages: Provide low resting pressure and high working pressure, which is key for effective fluid movement during muscle activity.
- Cohesive Layer: Keeps the bandages secure and maintains the compression level throughout the day.
This combination creates a “working pressure” when muscles contract, helping to push lymph fluid back toward the central lymphatic system, while the “resting pressure” is low enough to be safe and comfortable even at night.
Benefits of Multi-Layered Compression for Lymphedema
- Effective Swelling Reduction: Multi-layered compression is clinically proven to reduce limb swelling more efficiently than single-layer or elastic compression garments.
- Improved Lymph Drainage: The sustained pressure encourages lymphatic fluid movement and absorption.
- Enhanced Comfort and Mobility: Properly applied, multi-layered compression allows for better mobility and less discomfort than traditional elastic bandages.
- Lower Risk of Infection: By keeping the skin dry and reducing fluid buildup, this method helps prevent cellulitis and other skin infections.
- Customizable for Each Patient: Bandaging can be tailored to fit unique limb shapes, making it suitable for a wide range of lymphedema cases.
How Multi-Layered Compression is Applied
- Assessment: A certified lymphedema therapist assesses the affected limb and measures for bandaging.
- Skin Preparation: The limb is cleaned, dried, and any open wounds are properly covered.
- Padded Layer: A soft, non-woven padding is applied to protect the skin and distribute pressure.
- Absorbent Layer: If needed, an absorbent material is added to manage excess fluid.
- Compression Bandages: Short-stretch bandages are wrapped in a spiral or figure-eight pattern, applying graduated pressure from the distal (farthest) part of the limb toward the trunk.
- Securing Layer: A cohesive or self-adhesive bandage secures the entire wrap, ensuring it stays in place during movement.
This process is typically repeated daily or several times per week, especially during the intensive phase of lymphedema therapy. As swelling decreases, patients may transition to custom-fit compression garments for maintenance.
Best Practices for Multi-Layered Compression
- Professional Guidance: Always have compression bandages applied by a trained lymphedema therapist to ensure proper technique and safety.
- Regular Monitoring: Monitor the skin for signs of irritation, redness, or breakdown. Report any concerns to your healthcare provider immediately.
- Consistent Use: Adherence to wearing schedules is key to successful outcomes.
- Skin Care: Moisturize daily with fragrance-free lotions, and keep the limb clean and dry.
- Exercise: Gentle, prescribed movements can enhance the effectiveness of compression by activating muscle pumps.
Frequently Asked Questions
- Is multi-layered compression painful? When applied correctly, it should be comfortable. Any pain or numbness should be reported to your therapist.
- Can I shower with compression bandages? Most bandages are not waterproof. Remove them before showering and reapply as directed.
- Are there alternatives to multi-layered compression? For long-term management, custom-fit compression garments, pneumatic pumps, and manual lymphatic drainage may be used as adjuncts, but multi-layer bandaging is the cornerstone for active swelling reduction.
Conclusion
Multi-layered compression remains one of the most effective treatments for managing and reducing lymphedema. By working closely with your healthcare team, following best practices, and staying informed about your treatment options, you can significantly improve your quality of life and minimize the impact of lymphedema. If you’re considering compression therapy, consult a certified lymphedema specialist to develop a personalized plan that’s right for you.